
The themes targeted by WP TIP over the years are fairly reflective of the interests of policy makers and orientations of the global policy discussion. Footnote 1 The results of these meetings are documented in project reports, working documents and publications, which mirror the opinions of all Working Party members across countries because they are typically approved by consensus. One of the most influential and internationally renowned bodies is the OECD Working Party on Technology and Innovation Policy (WP TIP), which has met more than 50 times since 1993, gathering twice-yearly all OECD member countries and partner economies which are represented by renowned experts delegated by relevant national and international agencies and academia. Various arenas and institutions around the world bring STI policy makers and academics together to discuss national policy approaches and ensure their international co-ordination, find inspiration for national policies and learn from other countries’ experiences. Thus, in order to understand the evolution of STI policies over time and identify major themes attracting stakeholders’ attention, there is a need for high-level, synthetic overviews that would also connect to the more granular levels. Consequently, most reviews of this policy domain either refer to general issues without deep immersion into details or focus on specific narrower aspects. Thousands of policy documents and analytical reports issued over decades across the globe reflect those considerations.
They have a horizontal character touching upon diverse policy fields, related to health, education, employment, migration, trade, taxation, infrastructure, investment, SMEs, competition, etc. Suppose the publisher was not profit-maximizing but was concerned with maximizing economic efficiency.Science, technology and innovation (STI) policies aim at contributing to relevant conditions at the international, national and regional levels to ensure long term economic growth and social welfare. If the author was paid $3 million instead of $2 million to write the book, how would this affect the publisher's decision regarding the price to charge? Explain.į.

In your graph, shade in the deadweight loss. At what quantity do the marginal revenue and marginal-cost curves cross? What does this signify?ĭ.
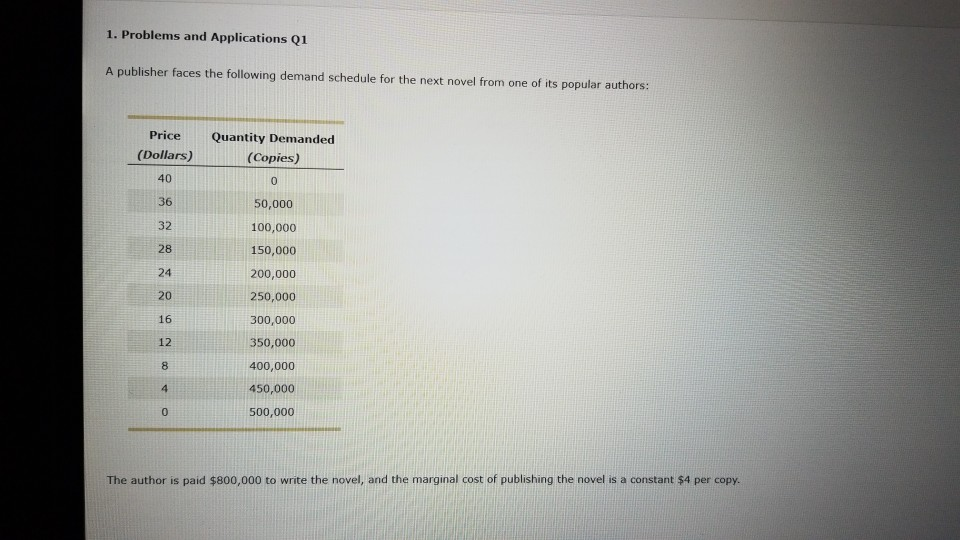
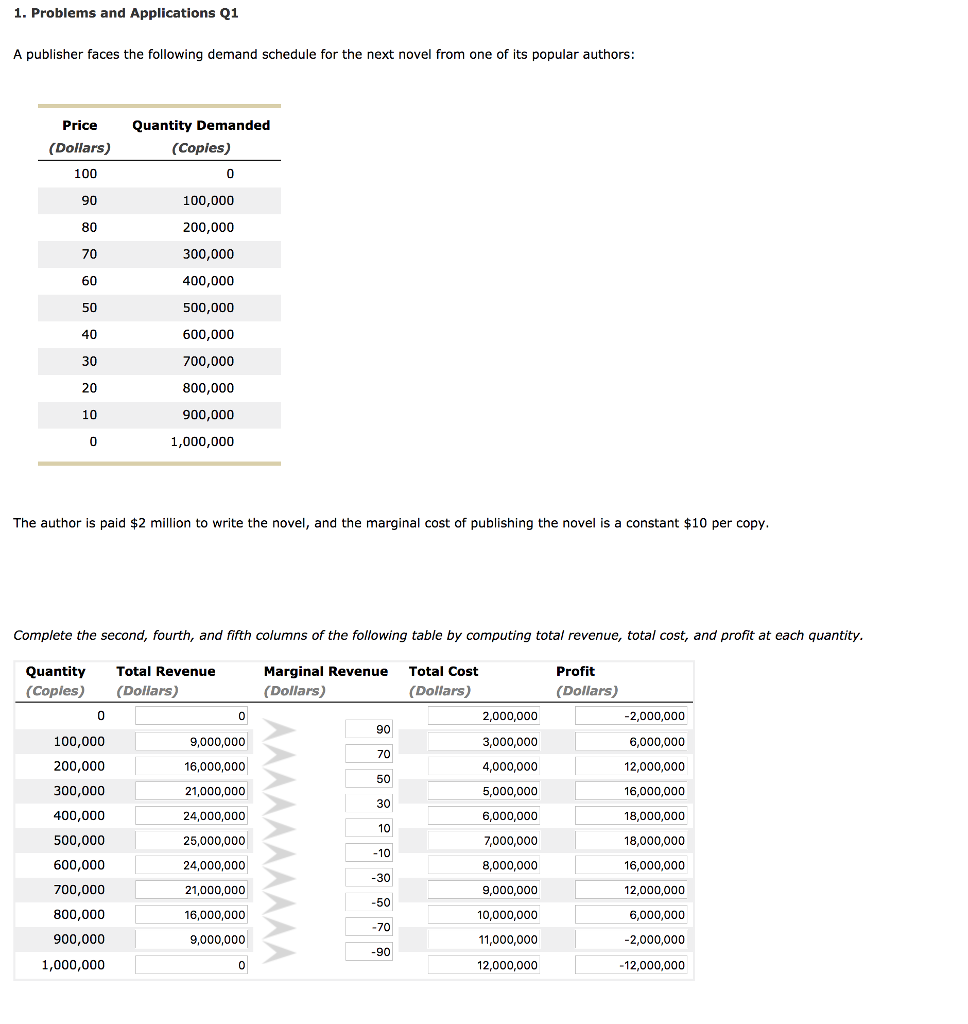
Graph the marginal-revenue, marginal-cost, and demand curves. (Recall that MR = /'J.TR//'J.Q.) How does marginal revenue compare to the price? ExplainĬ. What quantity would a profit-maximizing publisher choose? What price would it charge?ī. Compute total revenue, total cost, and profit at each quantity. The author is paid $2 million to write the book, and the marginal cost of publishing the book is a constant $10 per book.Ī. A publisher faces the following demand schedule for the next novel from one of its popular authors


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
